
The Ultimate Guide to Budgeting and Cost Control in Project Management
Cost control is an essential part of business strategy, yet it’s one of project managers’ most common challenges. According to the Project Management Institute’s report, organizations lose an average of 11.4% of their investments due to poor project performance, often tied to ineffective budgeting and cost control.
Today, many companies focus on upgrading their project management processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs. However, improvements can be challenging if you’re unsure where to begin, especially with outdated systems or compliance requirements. Here’s where the concepts of project budgeting and cost control come into action.
| Project budgeting is allocating financial resources to specific tasks and activities within a project. It requires the project managers to estimate all costs associated with the project and set a financial limit to ensure that the project is completed within the approved budget.
Cost control is the ongoing process of monitoring and managing expenses throughout the project lifecycle. It ensures that spending aligns with the budget and helps prevent cost overruns. |
The Importance of Creating the Right Budget and Cost Control in Project Management

A well-defined budget is crucial for your project’s success. Here’s why establishing an accurate budget and implementing effective cost control is essential:
1. Financial Clarity and Resource Allocation
A thorough budget provides a clear picture of available financial resources, enabling efficient allocation. Understanding where money is spent ensures that each project component, including team members and necessary tools, has what it needs to succeed.
This clarity will help you avoid misallocation and promote effective decision-making.
2. Prevention of Cost Overruns
Setting spending limits is a fundamental function of budgeting. By establishing clear financial boundaries, a well-structured budget will help you prevent excessive costs and help with disciplined financial decision-making.
3. Risk Mitigation and Informed Decision-Making
A good budget includes assessments of potential risks and keeps extra funds set aside for unexpected costs. This will help you avoid financial surprises and make better decisions.
You can make informed choices regarding the project’s goals, timelines, and resources while adhering to budget constraints.
4. Stakeholder Communication and Accountability
A well-defined budget enhances transparency and trust by clearly communicating financial expectations to stakeholders. Open communication is important for maintaining strong relationships and ensuring that everyone is aligned with project goals.
Furthermore, a budget promotes accountability since it assigns specific financial responsibilities to team members, holding them accountable for their spending and resource use.
5. Performance Measurement and Long-Term Planning
Budgets serve as benchmarks for evaluating performance. By tracking actual spending against planned expenditures, you can identify variances and areas for improvement.
Continuous assessment helps long-term planning by refining estimates for future projects based on past performance.
6. Broader Business Impact
Poor cost control can lead to financial strain, missed opportunities, and a loss of competitive advantage for businesses.
Effective budgeting impacts an organization’s overall profitability and long-term strategic objectives. Delivering a project within budget enhances the company’s reputation and frees up resources for other projects on time, contributing to overall business growth.
7. Effective Cost Control
Cost control involves continuously monitoring expenses to ensure they align with the budget. This framework will allow you to identify the variances at an early stage, and assist you in taking timely corrective actions. Effective cost control helps with:
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly track expenses throughout the project lifecycle.
- Early Detection of Variances: Identify deviations early for timely corrective measures.
- Informed Decision-Making: Use cost data to make critical decisions regarding resources and timelines.
- Resource Optimization: Efficient allocation of resources avoids waste and improves performance.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Consistent cost control builds trust by demonstrating responsible financial management.
Steps to Create a Budget

To prepare your project budget effectively, consider these five important factors:
1. Determine Activity Cost Estimates
Detailed Estimation: Begin by estimating costs associated with each project activity, including direct (materials, labor, equipment) and indirect (overhead) costs. Ensure that variations in cost are accounted for due to market fluctuations or unique project requirements to establish a flexible budget framework.
Historical Data Analysis: Use historical data from similar projects to enhance the accuracy of your cost estimates. This will help you identify potential financial discrepancies early and adjust your estimates accordingly.
Breakdown Structure: Use a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to categorize activities, facilitating precise cost estimation. The WBS should detail every step of the project from initiation to completion, ensuring that all tasks are accounted for and appropriately funded.
2. Document Basis of Estimates
Documentation of Assumptions: Carefully document the assumptions and methodologies used for cost estimates, specifying the sources of your data, the methods of calculation employed, and potential scenarios that could affect the project costs. This should include detailed rationales for each assumption to support transparency and facilitate future audits or reviews.
Review and Validation: Systematically engage stakeholders in reviewing the documented estimates to ensure a consensus on the methodologies and assumptions. This step should involve cross-functional teams, including finance, project management, and technical experts, to cover all perspectives and enhance the validation process.
3. Define Scope Baseline
Define Deliverables: Clearly outline project deliverables, including detailed specifications, critical milestones, and performance criteria, to be a definitive reference for tracking project progress and ensuring compliance with expected standards.
Prevent Scope Creep: Establish firm boundaries and implement a structured change control process that requires formal review and approval for all modifications to the project scope. This will safeguard against budget overruns and project delays.
4. Plan Project Schedule
Integrate Timing with Costs: Develop a comprehensive schedule that aligns project activities with their associated costs. This integration is crucial for effective cash flow management, ensuring that financial resources are available when needed to meet project demands without disruption.
Milestones and Deadlines: Identify and document critical milestones and associated deadlines. Use these milestones to schedule periodic budget reviews and necessary adjustments, maintaining financial control and project alignment with planned objectives.
5. Outline Resource Calendars
Outline Resource Availability: Create detailed resource calendars that track the availability of specific resources, such as personnel, equipment, and materials, throughout the project lifecycle. Doing this ensures that all resources are appropriately allocated when and where they are needed.
Optimize Resource Utilization: Strategically plan resource deployment to prevent over-allocation and under-utilization. This balanced approach promotes optimal project efficiency and resource management, contributing to the project’s overall success and timeline adherence.
Methods of Cost Control in Project Management

Effective cost control is vital for keeping projects within budget. Here are several methods that you can utilize:
1. Baseline Budget
Establishing a Reference Point: The baseline budget serves as the reference point against which all project spending is measured. By establishing this baseline at the project’s beginning, you can systematically compare actual expenditures to planned costs.
Tracking Performance Over Time: Regularly reviewing the baseline budget allows you to track performance over time, identifying trends and deviations that may signal future issues.
2. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Integration of Key Metrics: Earned Value Management (EVM) integrates project scope, schedule, and cost to evaluate project performance and provide an overall view of the project’s health.
| Key Metrics | Indication |
| Cost Performance Index (CPI) and | A CPI greater than 1 indicates that the project is under budget, while a CPI less than 1 signals overspending. |
| Schedule Performance Index (SPI) | An SPI greater than 1 shows that the project is ahead of schedule, while an SPI less than 1 indicates delays. |
Data-Driven Decision-Making: EVM helps teams to make informed, data-driven decisions to keep projects within budget and adjust plans as necessary.
3. Cost Variance
Measuring Financial Health: Cost variance measures the difference between planned and actual costs. This metric allows you to identify areas where spending exceeds expectations.
Facilitating Early Intervention: By recognizing cost variances early, you can implement corrective actions to address potential issues, such as reallocating resources or adjusting project scope.
4. Regular Financial Reviews
Scheduled Check-Ins: Conducting regular financial reviews throughout the project lifecycle will allow you to reassess budgets and spending patterns, ensuring the spending is aligned with the project goals.
Identifying Trends: These reviews help identify trends and potential financial risks, enabling proactive adjustments before issues escalate.
5. Change Control Process
Formal Approval for Changes: Establishing a change control process ensures that the upper management and stakeholders formally review and approve any project scope or budget modifications. This helps prevent unauthorized spending and scope creep.
Impact Analysis: Evaluate the financial impact of proposed changes before approval, ensuring that the adjustments suggested are justifiable and align with overall project objectives.
6. Contingency Planning
Setting Aside Funds: Allocating contingency funds within the budget will prepare your team for unexpected costs and risks. This “safety net” can be crucial in managing uncertainties effectively.
Risk Assessment: Conduct regular risk assessments to determine if the contingency funds are adequate and adjust as needed based on project conditions.
7. Use of Financial Software Tools
Real-Time Monitoring: Using financial software tools allows for real-time monitoring of expenses and budget adherence. These tools often provide dashboards that visualize spending patterns and highlight discrepancies.
Automation of Reports: Automated reporting features can generate financial performance reports quickly, helping with timely decision-making and resource allocation adjustments.
How to Keep Your Projects Within Budget?
- Implement Real-Time Tracking Tools: Utilize project management tools that offer real-time tracking of expenses. These tools help monitor actual spending against the budget, providing immediate visibility into financial performance.
- Conduct Regular Budget Reviews: Schedule budget reviews at important project milestones to assess financial health. This proactive approach helps ensure alignment between project progress and budget expectations.
- Monitor Resource Allocation: Effective resource management is crucial to staying within budget. Ensure that personnel and materials are utilized efficiently to avoid waste and unnecessary expenses.
- Adapt to Changing Circumstances: Flexibility is essential in today’s dynamic project environment. Be prepared to adjust budgets in response to changing market conditions, client demands, or regulatory requirements.
- Proactive Risk Management and Cost Control: Proactive risk management involves identifying potential financial risks before they escalate into major issues. By continuously assessing risks and updating contingency plans, you can maintain financial viability even when unexpected challenges arise. Implementing an EVM framework supports proactive risk management by enabling early detection of variances, allowing for timely adjustments.
How evData Pro Enhances Budgeting and Cost Control in Project Management?
evData Pro provides an extensive suite of tools that simplify budgeting and cost control for project managers and financial teams. By offering intuitive dashboards, advanced reporting features, and real-time tracking, evData Pro ensures project budgets are monitored effectively and aligned with performance goals.
Here’s how evData Pro contributes to successful budget management:
1. Interactive Dashboards for Real-Time Insights
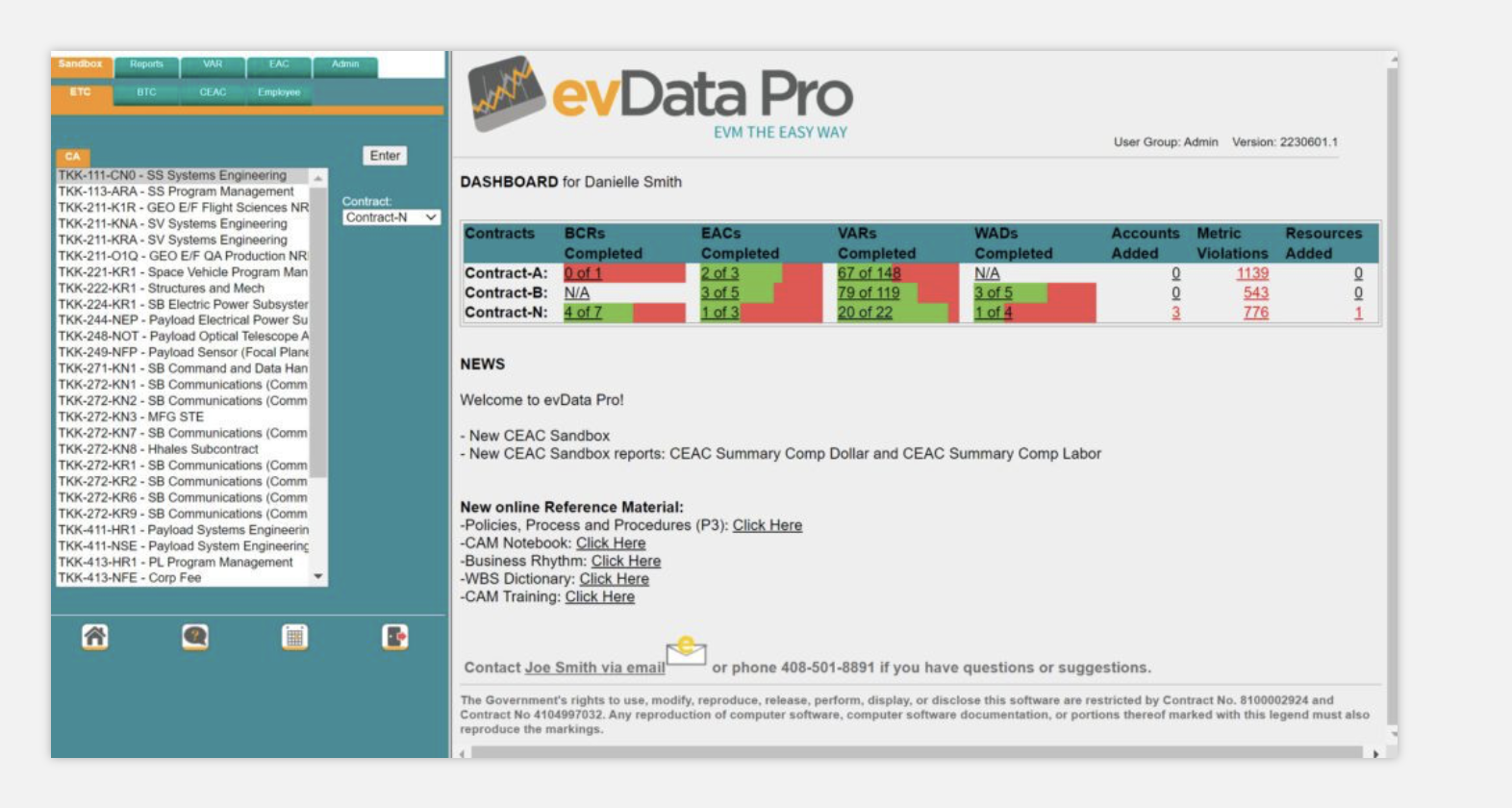
The evData Pro Dashboard offers a color-coded interface that presents a real-time overview of project performance, including tasks completed and outstanding. You can instantly see when thresholds are violated and drill down into key data to investigate the cause behind performance metrics. This ensures that cost overruns are detected early, allowing for timely corrective action.
2. Comprehensive Budget Reporting
With evData Pro, you can access over 100 standard reports, including those tracking budget performance at the WBS, OBS, and work package levels. These reports break down elements of cost, enabling you or other cost managers to compare estimated costs with actuals across multiple levels, such as contract, employee, and account.
3. Head Count and Rate Analysis
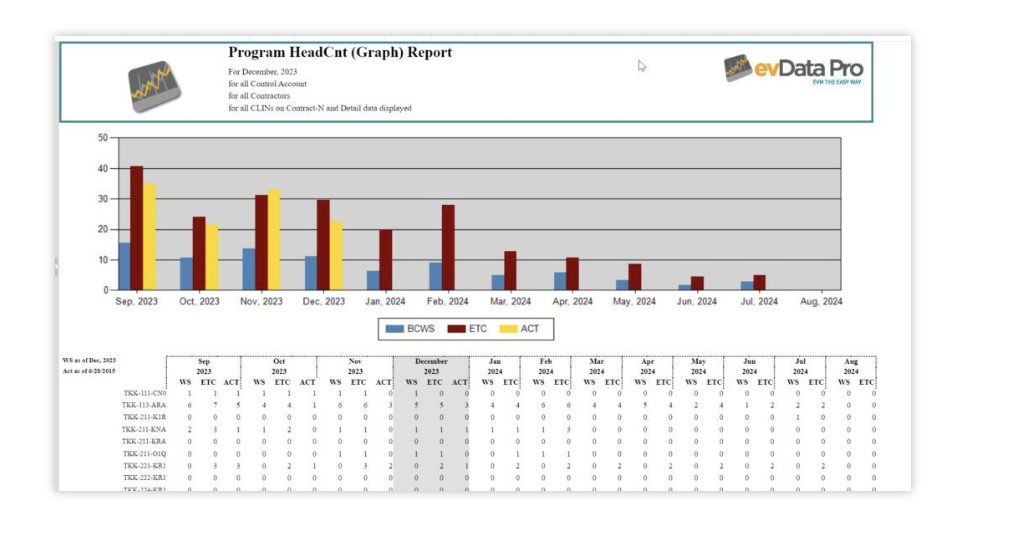
Headcount Reporting allows you to determine employee utilization across contracts and organizations. By comparing staffing plans to budgets and actuals, evData Pro ensures that labor costs are optimized.
Additionally, Rate Analysis distinguishes whether cost issues stem from labor rates or volume, helping to pinpoint areas for improvement and prevent unnecessary budget increases.
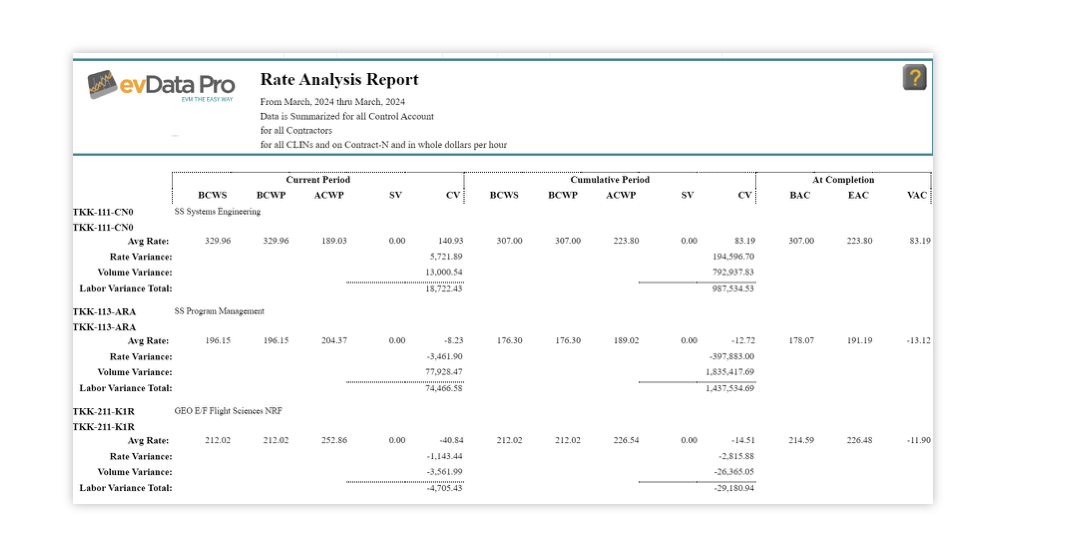
4. Variance Analysis and Corrective Action
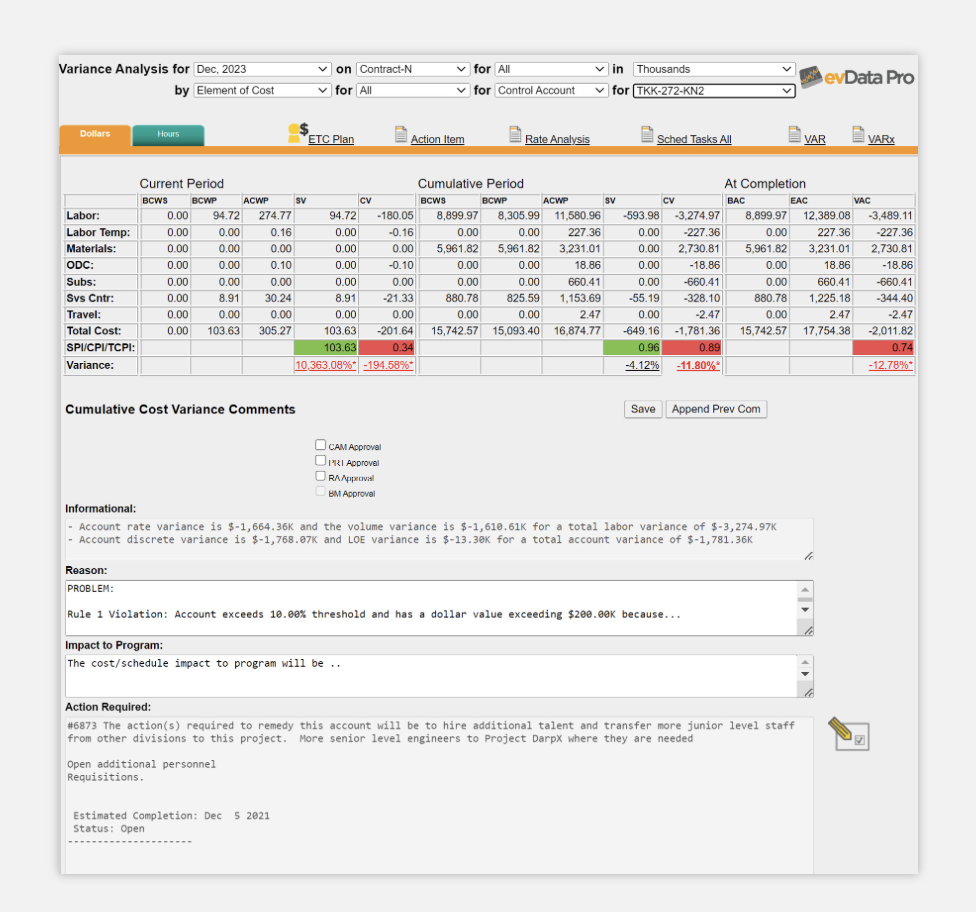
evData Pro provides detailed variance analysis at the OBS, WBS, and control account levels. With automated notifications for violations, you can respond quickly to cost variances by documenting the reasons, impacts, and necessary corrective actions.
5. Baseline Change Request (BCR) Management
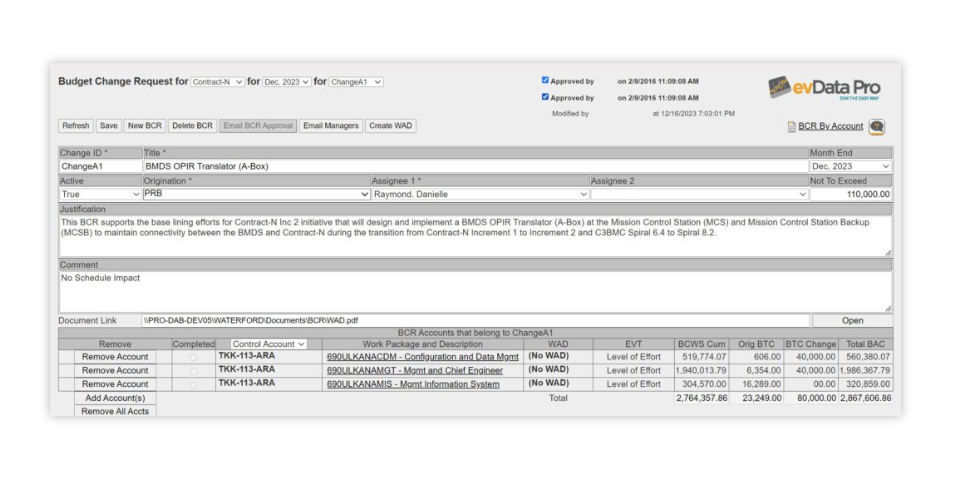
evData Pro’s Baseline Change Request (BCR) functionality allows you to efficiently manage budget changes. By tracking changes from the BCR stage through to completion, project teams can maintain control over evolving project requirements while ensuring that the budget remains aligned with overall objectives.
6. Sandbox for Budget Planning
The evData Pro Sandbox offers a flexible environment where you can adjust your budgets without affecting existing estimates. This feature allows for forward planning by generating new Estimate to Completion (ETC), Budget at Completion (BAC), or Consolidated Estimate at Completion (CEAC) figures. As a project or cost manager, you can plan using multiple views and breakdown structures, ensuring accurate forecasting and cost control.
Get Started on Smarter Budgeting with ProboData!
Effective budgeting and cost control are essential for project success, and ProboData is here to help you achieve these goals. With its powerful features for real-time tracking, accurate cost estimation, and comprehensive reporting, evData Pro provides the tools you need to manage your project’s finances effectively.
Don’t let budgeting challenges derail your project. Contact ProboData today to learn how evData Pro can enhance your project management strategy. Our team is ready to help you optimize your budgeting and cost control processes, ensuring your projects stay on track and within budget.
Contact us at ProboData for more information or to schedule a demo.
