
What Is Project Schedule Variance and How to Calculate It?
Project management is all about precision—hitting deadlines and managing budgets effectively. At ProboData, we understand that the difference between project success and failure often hinges on effective time management. However, despite the best-laid plans, about 50% of all projects still experience delays, mainly due to scheduling challenges.
One of the most effective tools for addressing this issue is project schedule variance, which is a critical indicator of the degree to which a project is ahead or behind its planned schedule.
By understanding and applying this metric, project managers can make informed decisions quickly, adjusting project timelines before small setbacks become costly delays. This blog will explore how project schedule variance is calculated and why it’s indispensable for maintaining project timelines effectively.
What Is Project Schedule Variance?
Project schedule variance is a critical metric used in earned value management to measure whether a project is ahead, behind, or precisely on schedule compared to the original plan. It helps you get a clear view of your project’s progress.
For example, a software development project scheduled to deploy 10 features over 5 months at a rate of 2 features per month. If, after three months, only 5 features are complete, the project’s schedule variance would be negative, signaling a need for corrective actions to meet the deadline. This insight allows project managers to adjust resources or processes effectively to align with project timelines.
How to Calculate Schedule Variance?
To calculate schedule variance (SV), you need two critical pieces of information:
- Earned Value (EV): It indicates the work completed so far.
- Planned Value (PV): It indicates the work planned to be completed by now.
The formula for schedule variance is:
SV = EV – PV
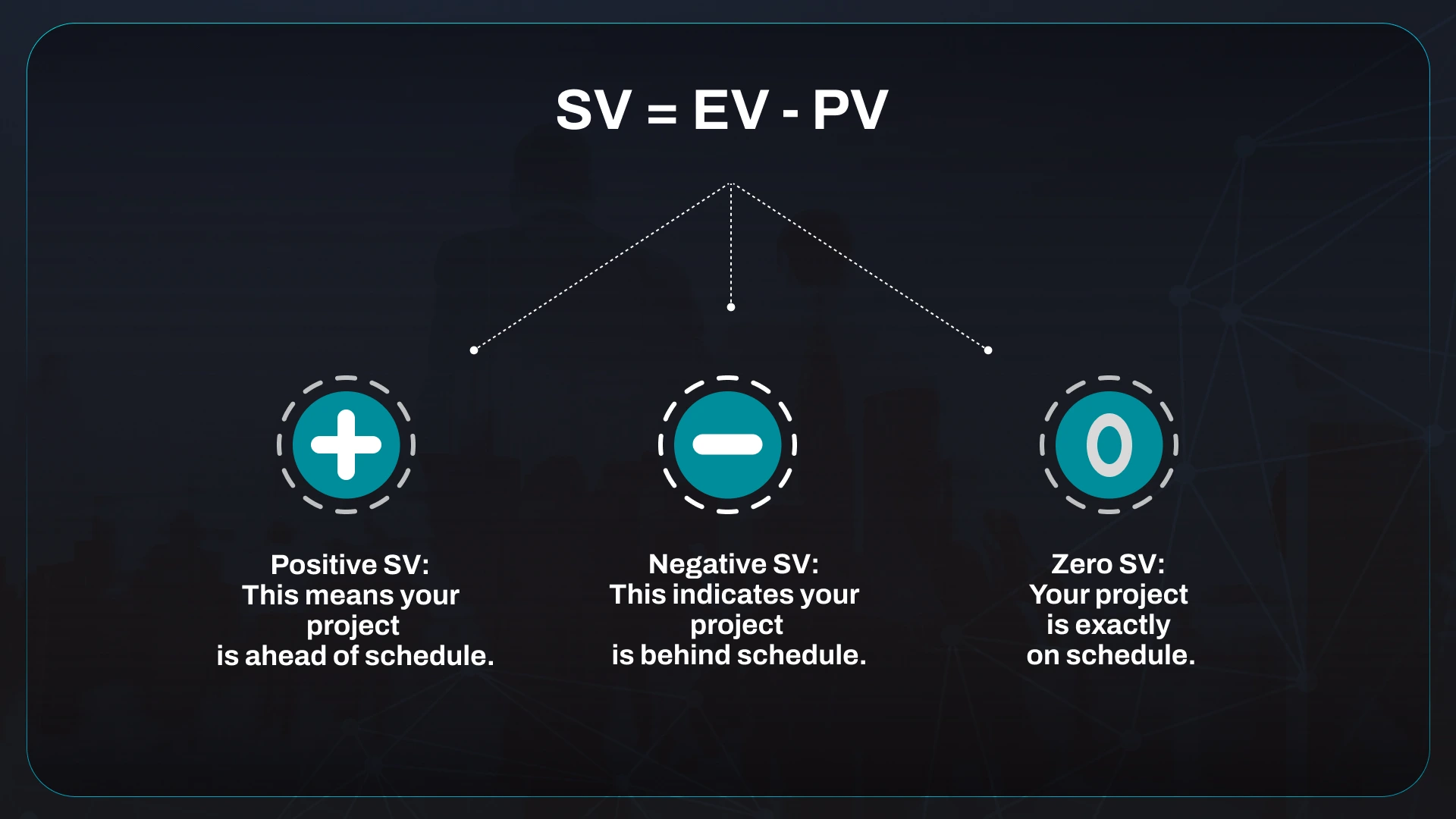
- Positive SV: This means your project is ahead of schedule.
- Negative SV: This indicates your project is behind schedule.
- Zero SV: Your project is exactly on schedule.
Example:
Suppose you’re working on a project that is supposed to be 50% complete at this point (planned value = 50%). However, after checking the progress, you see that only 40% of the work has been completed (earned value = 40%).
Using the formula:
SV = 40% – 50% = -10%
This means your project is 10% behind schedule.
Understanding Project Schedule Variance Across Project Phases
Project schedule variance can signify different challenges and milestones depending on the project’s stage. Let’s break down what this means at different points in the project:
1. Early Phase
In the initial stages of a project, encountering a schedule variance is common as teams are just ramping up and unforeseen challenges may arise. Although these variances might seem minor, addressing them promptly is crucial. Early detection and correction prevent these deviations from escalating, ensuring the project remains on track without significant disruptions.
2. Mid-Phase
By the project’s midpoint, the goal is to achieve a schedule variance near zero, indicating that the project is progressing according to the planned schedule. A variance far from zero at this phase suggests a need for immediate corrective actions, such as reallocating resources or revising timelines, to realign the project with its scheduled milestones.
3. End Phase
In the final phase, schedule variance should ideally be zero or slightly positive. A zero or positive means the project is either on time or ahead of schedule, which is an excellent position as you near the final deliverables.
The Benefits of Tracking Project Schedule Variance
![]()
There are several benefits of tracking project schedule variance:
1. Early Problem Detection
By regularly calculating schedule variance, you can detect problems early. This gives you more time to fix delays before they become unmanageable.
2. Better Budget Control
Time is money in project management. If you’re behind schedule, you might also be overspending. Schedule variance helps you see the connection between time and cost.
3. Improved Decision Making
Knowing whether your project is on schedule allows you to make informed decisions. Should you add more resources? Change the timeline? Knowing the schedule variance helps answer those questions.
What Causes Negative Schedule Variance?

Several factors can contribute to a project falling behind its planned schedule. Here are some common culprits of negative schedule variance:
- Scope Changes: Introducing new tasks or expanding project requirements often leads to delays. Even minor adjustments can significantly derail progress.
- Resource Shortages: Not having enough people, materials, or equipment can slow things down and delay project completion.
- Inefficient Processes: Ineffective task management or operational bottlenecks can disrupt workflow, causing significant setbacks.
- External Factors: Unpredictable elements like adverse weather, fluctuating market conditions, or disruptions in the supply chain can also impact project timing.
How Can You Manage Negative Schedule Variance?

Below are some effective strategies for keeping your project on track and preventing delays from spiraling out of control.
1. Frequent Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for identifying deviations early in the project’s lifecycle. Schedule variance is a dynamic metric that can shift as the project progresses. By checking in on the project’s schedule frequently, you can calculate schedule variance in real time and identify potential issues before they worsen.
For example, if you calculate Schedule Variance weekly, you can spot a 5% delay early on and take action rather than discovering a 20% delay much later. Early detection means you can make adjustments while they’re still manageable, helping to steer your project back on course.
2. Prioritize Important Tasks
Not all tasks in a project have the same level of urgency. Some are directly tied to the project’s overall completion, while others are more flexible. This is where the concept of the right path comes into play.
Focusing on the most important tasks—those that are part of the right path—helps ensure the project stays on schedule. By prioritizing these tasks, you minimize the risk of falling behind in the areas that matter most.
If non-essential tasks are running behind, you might still be able to finish on time, but if important tasks are delayed, the entire project could be pushed past its deadline.
3. Improve Resource Allocation
A common cause of negative schedule variance is inadequate resource allocation. If certain tasks are falling behind, it might be because they don’t have enough people, time, or materials to complete them on schedule. One way to address this is by reallocating resources from tasks on or ahead of schedule to those falling behind.
This doesn’t always mean adding more team members. It could involve adjusting work hours, providing additional equipment, or even shifting priorities within the team. Proper resource allocation ensures that important tasks are not left under-resourced, helping the project move forward without unnecessary delays.
4. Adjust the Schedule
If your project consistently falls behind schedule, it may be necessary to reevaluate your timeline. Significant negative schedule variance often signals that deadlines need adjustment or that certain tasks require more time than initially planned. Adapting your schedule helps address these discrepancies, keeping your project on track toward its goals.
However, simply extending deadlines isn’t always the best solution. Instead, consider breaking larger tasks into smaller, more manageable parts. This allows for a more accurate assessment of progress and makes it easier to track if you’re back on schedule after the adjustment.
Communicate any changes to the schedule to the entire team so that everyone is aware of updated deadlines and expectations.
5. Improve Communication
Poor communication is a major contributor to project delays. Team members may not be aware of shifting priorities, upcoming deadlines, or even the progress of other team members. Improving communication can significantly reduce the risk of negative schedule variance.
Hold regular project meetings to review task status, discuss potential roadblocks, and ensure everyone is aligned with the project timeline. Encourage open lines of communication so that team members feel comfortable reporting delays or issues as soon as they arise.
Good communication also ensures that all stakeholders are informed about the project’s progress, making managing expectations easier and reducing pressure on the project team.
The Role of evData Pro in Managing Schedule Variance
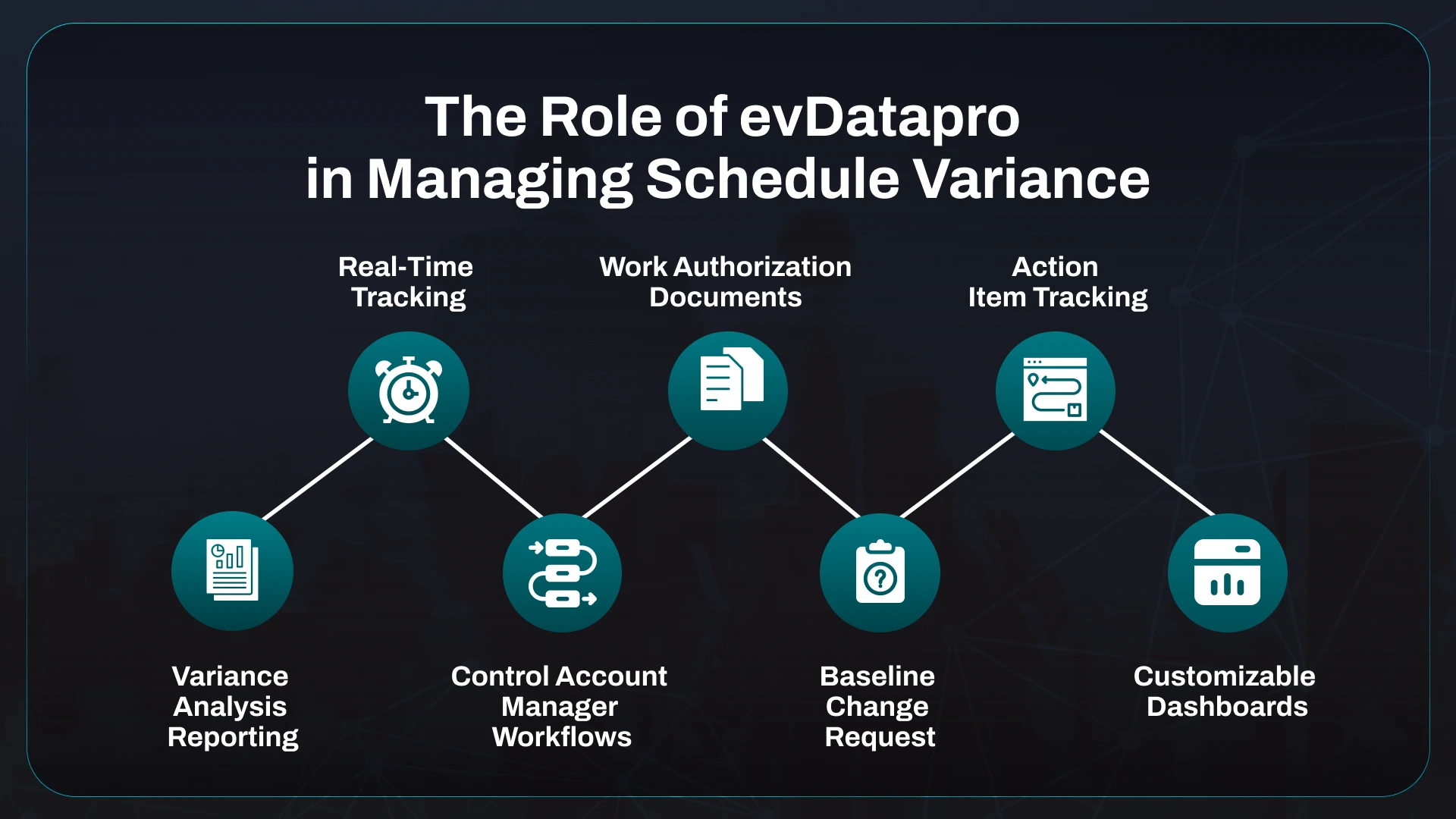
Having the right tools can make a huge difference in managing schedule variance. ProboData’s evDatapro offers powerful project management features to help you stay on schedule and manage variance effectively.
Variance Analysis Reporting
Enables CAMs and finance managers to document explanations about cost and schedule variances for current, cumulative, and at completion periods. Variance analysis reporting is crucial for controlling schedule variances by providing detailed insights into the reasons behind deviations.
Real-Time Tracking
Allows monitoring of project progress in real-time, enabling quick detection and response to schedule changes.
Control Account Manager Workflows
These workflows integrate technical scope, schedule, and budget, which is essential for effectively managing and tracking schedule variance.
Work Authorization Documents
These documents track budget and management assignment changes over the contract’s life. They support the effective tracking of schedule adherence, ensuring that all adjustments are correctly documented and aligned with project objectives.
Baseline Change Request
BCRs enable users to initiate and document budget changes and the accounts tied to those changes, effectively managing adjustments that can impact the project schedule. This process ensures that all modifications are tracked and aligned with the project’s financial and scheduling objectives, facilitating controlled updates to the project baseline.
Action Item Tracking
Provides visibility into the history of every action taken via corrective action logs, which is important for addressing factors contributing to schedule variance.
Customizable Dashboards
These dashboards provide a user-friendly interface, enabling easy access to project progress and key metrics related to schedule variance. Customize your dashboard to monitor and manage critical data effectively, ensuring you have the insights needed to steer project success.
Optimize Your Project Management with ProboData!

Navigating project schedules effectively is crucial for meeting deadlines and maintaining budgets. ProboData’s evData Pro helps you with sophisticated earned value management (EVM) tools to streamline project schedule management.
Don’t let scheduling variances set you back. Equip your team with evData Pro to harness comprehensive control over your project schedules, anticipate challenges, and drive successful outcomes. Explore how our targeted features can empower your project management efforts and help you maintain tight control over every project phase, ensuring on-time and on-budget delivery.
